In today’s world, where information is exchanged and stored digitally, the need for secure communication and protection of sensitive data has become crucial. This is where cryptography comes into play, providing a way to safeguard information and ensure its authenticity. In this article, we will take a deep dive into the realm of secret codes, exploring the fundamental concepts, types, techniques, and applications of cryptography. So, let’s begin our journey into the fascinating world of cryptography.
What is Cryptography?
At its core, cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of adversaries. It involves transforming plain text into a coded form, known as ciphertext, using mathematical algorithms and keys. The primary goal of cryptography is to make the information unreadable to anyone who does not have the key to decrypt it. In simpler terms, it converts the information into a secret code that can only be understood by authorized parties.
The word “cryptography” is derived from the Greek words kryptós, meaning “hidden,” and gráphein, meaning “to write.” The concept of cryptography dates back to ancient times when people used various methods to protect their secrets. The famous Caesar cipher, used by Julius Caesar, was one of the earliest forms of cryptography. It involved shifting each letter of a message by a fixed number of positions in the alphabet.
Types of Cryptography

Cryptography can be broadly classified into two main types – symmetric and asymmetric cryptography.
Symmetric Cryptography
Also known as private-key cryptography, symmetric cryptography uses a single secret key for both encryption and decryption of messages. This means that the sender and receiver share the same key, which is kept confidential to maintain the security of the communication. The most commonly used symmetric encryption algorithm is the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), which uses a 128-bit key to encrypt data.
One of the main advantages of symmetric cryptography is its efficiency in terms of speed and processing power. However, it also has its drawbacks, such as the need to distribute the secret key securely to all parties involved in communication.
Asymmetric Cryptography
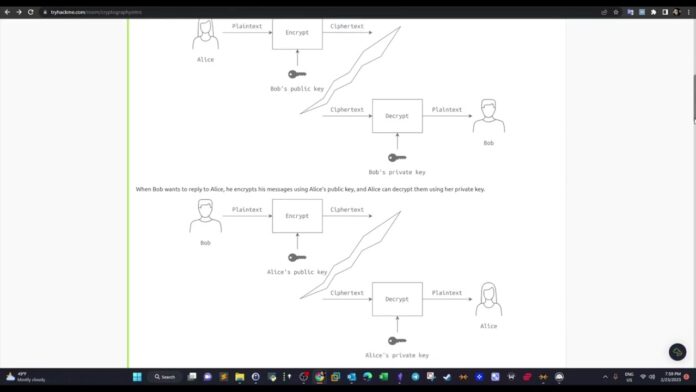
Asymmetric cryptography, also known as public-key cryptography, uses two different keys – a public key and a private key – for encryption and decryption, respectively. The public key is freely available to everyone, while the private key is kept confidential by the owner. This method eliminates the need for key distribution, one of the main challenges faced in symmetric cryptography.
The most commonly used asymmetric encryption algorithm is the Rivest-Shamir-Adleman (RSA) algorithm, which uses a combination of prime numbers to generate the public and private keys. Asymmetric cryptography is relatively slower than symmetric cryptography but offers better security and is widely used in applications such as digital signatures and secure online transactions.
Cryptographic Algorithms and Techniques

Cryptography relies on various algorithms and techniques to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of information. Let’s take a look at some of the most common cryptographic algorithms and techniques used today.
Hash Functions
Hash functions are mathematical algorithms that convert an input of any size into a fixed-size output, known as a hash value or digest. These algorithms are one-way, meaning that it is nearly impossible to derive the original input from the hash value. Hash functions are widely used in cryptography for data integrity checks, password storage, and digital signatures.
Some popular hash functions include Secure Hash Algorithm (SHA) and Message Digest (MD).
Data Encryption Standard (DES)
DES is a symmetric key block cipher algorithm developed by IBM in the 1970s. It uses a 56-bit key to encrypt blocks of plain text into ciphertext. DES was widely used for encryption in the past, but due to its small key size, it is now considered insecure and has been replaced by the more robust Advanced Encryption Standard (AES).
Digital Signatures
Digital signatures are used to ensure the authenticity and integrity of digital documents or messages. They work by applying a mathematical algorithm to a message, creating a unique signature that can be verified using the sender’s public key.
Pretty Good Privacy (PGP)
PGP is a hybrid encryption technique that combines both symmetric and asymmetric cryptography. It uses a combination of encryption keys to secure messages and files. PGP is commonly used for email encryption, as well as in securing online transactions and communication.
Applications of Cryptography
Cryptography finds its use in various fields and applications, such as:
Secure Online Transactions
One of the most common applications of cryptography is in securing online transactions. E-commerce websites, online banking, and other financial transactions use secure protocols such as SSL and TLS, which utilize various cryptographic algorithms to protect sensitive information.
Password Protection
Cryptography is also used to store and protect passwords in databases. Hash functions are used to convert passwords into hash values, making it difficult for hackers to obtain the original passwords.
Digital Signatures
Digital signatures are widely used to ensure the authenticity of digital documents and messages. They are essential in areas such as online contracts, legal documents, and electronic voting systems.
Data Protection
Cryptography plays a crucial role in protecting data from unauthorized access. It is used in file and disk encryption to ensure that only authorized users have access to confidential information.
Future Trends in Cryptography
As technology continues to advance, new trends and developments are emerging in the world of cryptography. Let’s take a look at some of the future trends in this field.
Post-Quantum Cryptography
With the rapid development of quantum computing, traditional cryptographic methods may no longer be sufficient to protect sensitive information. Post-quantum cryptography is an area of research that focuses on developing encryption techniques that are resistant to quantum computing attacks.
Homomorphic Encryption
Homomorphic encryption is a form of cryptography that allows computations to be performed on encrypted data without the need for decryption. This enables secure data processing in untrusted environments, making it a valuable tool for cloud computing and other online services.
Conclusion
Cryptography plays a vital role in today’s digital world, ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of our information. From ancient methods such as the Caesar cipher to modern encryption algorithms like AES and RSA, cryptography has come a long way. With the constant evolution of technology, new challenges arise, leading to the development of advanced cryptographic techniques. As we continue to rely more and more on digital communication and transactions, the importance of cryptography will only continue to grow.