In today’s digital age, understanding cybersecurity is crucial for protecting personal and professional information. This article, “Cybersecurity 101: Essential Basics You Need to Know,” explores the fundamentals of cybersecurity, its definition, and its importance. It delves into common cyber threats and vulnerabilities, offering insights into basic cybersecurity measures and best practices. Additionally, it covers essential topics such as password management, authentication techniques, encryption, and data protection. The article also highlights the importance of regular software updates, patch management, and safe browsing and email security practices, providing a comprehensive guide to help you safeguard your digital presence.
uzocn.com will lead a thorough examination of this topic.
1. Understanding Cybersecurity: Definition and Importance
Cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from digital attacks. These attacks are often aimed at accessing, changing, or destroying sensitive information, extorting money from users, or interrupting normal business processes. As our reliance on technology grows, so does the importance of securing our digital infrastructure. Cybersecurity is not only about protecting confidential information but also about ensuring the reliability and integrity of data and systems that support everyday activities.
The importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. In a world where data breaches and cyber attacks are increasingly common, organizations and individuals must be vigilant in safeguarding their digital assets. A successful cyber attack can lead to significant financial losses, reputational damage, and even legal repercussions. Moreover, with the rise of interconnected devices and the Internet of Things (IoT), the attack surface for cyber threats has expanded, making robust cybersecurity measures more critical than ever.
Understanding cybersecurity is the first step in building a resilient defense against cyber threats. By recognizing its importance and implementing fundamental cybersecurity practices, individuals and organizations can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to cyber attacks and ensure the safety and integrity of their digital environments.
2. Common Cyber Threats and Vulnerabilities
Cyber threats and vulnerabilities come in various forms, each posing significant risks to personal and organizational security. Common cyber threats include malware, phishing, ransomware, and denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Malware, such as viruses, worms, and trojans, can infiltrate systems, causing damage or unauthorized access. Phishing attacks deceive individuals into providing sensitive information, often through fraudulent emails or websites. Ransomware encrypts a victim’s data, demanding payment for its release, while DoS attacks overwhelm systems, rendering them inoperable.
Vulnerabilities are weaknesses in systems or software that can be exploited by cyber attackers. These can result from outdated software, weak passwords, or unpatched security flaws. For instance, failing to apply security updates and patches can leave systems exposed to known exploits. Weak passwords and poor authentication practices also make it easier for attackers to gain unauthorized access.
Understanding these threats and vulnerabilities is crucial for developing effective cybersecurity strategies. By staying informed about the latest threats and regularly updating security measures, individuals and organizations can better protect themselves against cyber attacks. Awareness and proactive measures are key to mitigating the risks posed by these common cyber threats and vulnerabilities.
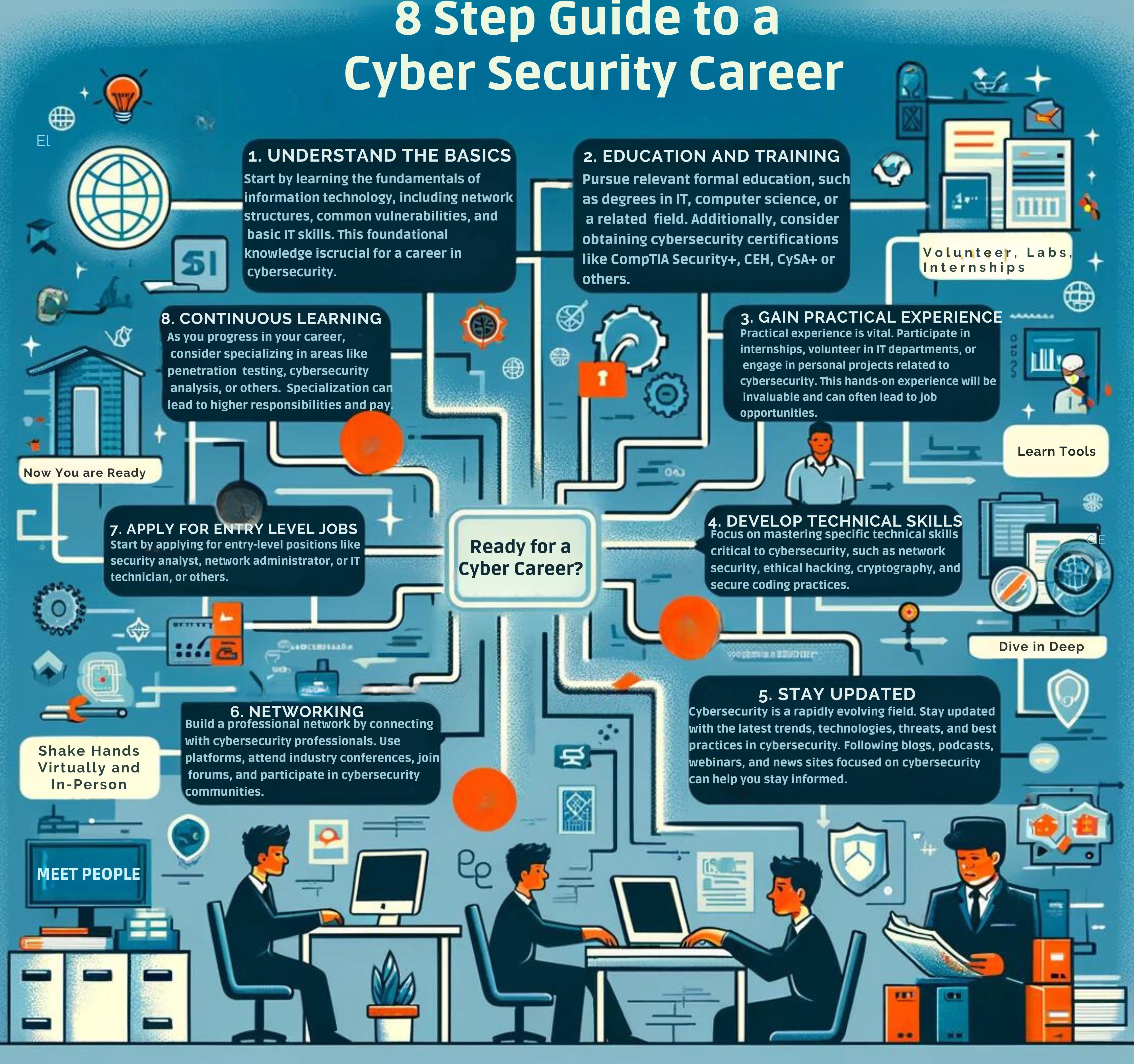
3. Basic Cybersecurity Measures and Best Practices
Implementing basic cybersecurity measures and best practices is essential for protecting against cyber threats. One fundamental practice is using strong, unique passwords for different accounts and regularly updating them. Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring additional verification steps beyond just a password.
Regularly updating software and applying patches is critical to address vulnerabilities and prevent exploits. Utilizing antivirus and anti-malware software helps detect and remove malicious programs. Firewalls act as a barrier between trusted and untrusted networks, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic.
Educating users about safe browsing habits and recognizing phishing attempts can prevent many cyber attacks. It’s important to avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading unverified attachments. Regularly backing up data ensures that, in the event of a ransomware attack or data loss, information can be restored without paying a ransom.
By adopting these basic cybersecurity measures and best practices, individuals and organizations can significantly enhance their defenses against cyber threats and safeguard their digital environments.

4. Password Management and Authentication Techniques

Effective password management and robust authentication techniques are vital components of cybersecurity. Creating strong, unique passwords for each account significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. Strong passwords typically include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters and avoid easily guessable information like birthdays or common words.
Using a password manager can help securely store and manage multiple passwords, ensuring that each one is both strong and unique. This tool can also generate random passwords, further enhancing security.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is an additional layer of protection that requires users to verify their identity through multiple means, such as a password and a temporary code sent to their mobile device. This makes it much harder for attackers to gain access, even if they manage to steal a password.
Regularly updating passwords and changing them immediately if a breach is suspected are critical practices. Avoiding the reuse of passwords across different sites also prevents a single compromised password from granting access to multiple accounts.
By implementing these password management and authentication techniques, individuals and organizations can significantly enhance their security posture and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access.
5. Introduction to Encryption and Data Protection
Encryption and data protection are fundamental to safeguarding sensitive information in the digital realm. Encryption involves converting data into a coded format that can only be deciphered with a specific key, ensuring that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties. This technique is widely used to protect information during transmission over networks and for data stored on devices.
There are two main types of encryption: symmetric and asymmetric. Symmetric encryption uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, making it faster but requiring secure key distribution. Asymmetric encryption, on the other hand, uses a pair of keys—a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption—enhancing security, especially for transactions over the internet.
Data protection extends beyond encryption. It includes measures such as secure data storage, regular backups, and access controls to ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive information. Implementing strong encryption standards and regularly updating encryption protocols are essential practices to counteract evolving cyber threats.
By understanding and utilizing encryption and data protection techniques, individuals and organizations can significantly enhance their ability to safeguard sensitive data, ensuring privacy and security in the digital age.
6. Importance of Regular Software Updates and Patch Management
Regular software updates and patch management are critical components of cybersecurity, vital for protecting systems against vulnerabilities and cyber threats. Software updates often include patches that address security flaws discovered in the software. Without these updates, systems remain susceptible to exploitation by cyber attackers who can use known vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access or cause damage.
Timely application of patches and updates ensures that security vulnerabilities are quickly addressed, minimizing the window of opportunity for attackers. This is particularly important for operating systems, web browsers, and other commonly used software, which are frequent targets for cyber attacks.
Automating updates and patch management processes can help ensure that systems are consistently protected without relying on manual intervention. However, it is also essential to test patches in a controlled environment before deployment to avoid potential compatibility issues that could disrupt operations.
By prioritizing regular software updates and effective patch management, organizations and individuals can significantly reduce their risk of cyber attacks, maintaining a more secure and resilient digital environment. Keeping software current is a proactive step in safeguarding against the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
7. Safe Browsing and Email Security Practices
Safe browsing and email security practices are essential to protect against cyber threats. When browsing the internet, it is important to visit only trusted websites and be cautious of clicking on links or downloading files from unfamiliar sources. Using a reputable web browser with built-in security features, such as blocking malicious websites and pop-up ads, can enhance protection.
Employing browser extensions that provide additional security, like ad blockers and anti-phishing tools, can further safeguard your online experience. Always ensure that the website URL begins with “https://” to confirm a secure connection.
Email security is equally crucial. Be wary of emails from unknown senders, especially those that contain attachments or links. Phishing attacks often disguise themselves as legitimate communications to steal sensitive information. Use email filters to detect and block spam and phishing attempts.
Regularly updating email passwords and enabling multi-factor authentication can provide an additional layer of security. Avoid sharing personal or sensitive information via email unless absolutely necessary and only with trusted recipients.
By adopting safe browsing habits and email security practices, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to cyber threats and maintain a more secure digital presence.
In conclusion, mastering the basics of cybersecurity is essential for protecting yourself and your data in the digital age. By understanding common threats, implementing basic measures, managing passwords, utilizing encryption, and staying updated on software and security practices, you can significantly enhance your defenses against cyber attacks and ensure a safer online experience.
uzocn.com
uzocn.com


